Pure Tone Audiometry (PTA) is one of the most widely used and trusted hearing evaluation methods across all age groups. It measures hearing sensitivity to different sound frequencies and volumes, helping identify the exact nature and extent of hearing loss. The test is painless, quick, and highly reliable – making it the first diagnostic step recommended by ENT specialists and audiologists.
If hearing loss is suspected due to aging, noise exposure, ear infections, tinnitus, dizziness, or difficulty understanding conversations, a pure tone audiometry test plays a crucial role in diagnosing and planning treatment. The report gained from PTA helps determine whether hearing aids, medical treatment, or further evaluations are needed.
Pure Tone Audiometry: What It Is and How It Measures Your Hearing?
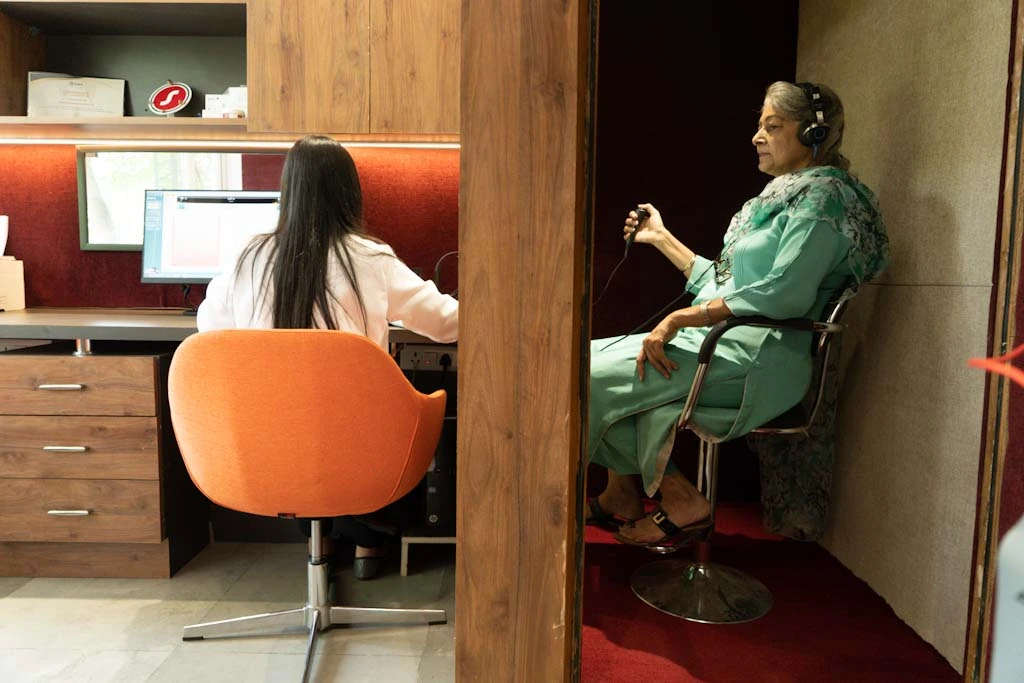
Pure tone audiometry (PTA), commonly known as the pure tone audiometry test, is a fundamental diagnostic tool used to evaluate an individual’s hearing sensitivity. It involves presenting pure tones-single-frequency sounds—at varying volumes through headphones or bone vibrators in a soundproof booth. Patients actively respond by raising a hand, pressing a button, or verbally indicating when they detect the sound, which helps plot precise auditory thresholds on an audiogram test. This subjective test is quick, reliable, and forms the backbone of hearing assessments worldwide.

Definition of PTA
Pure tone audiometry (PTA) is a subjective behavioral test that measures the quietest sounds a person can hear across a range of frequencies, typically from 250 Hz (low-pitched) to 8,000 Hz (high-pitched). These pure tones mimic everyday sounds like speech consonants or environmental noises. Unlike objective tests, PTA relies on patient cooperation, making it ideal for adults and cooperative children, and it provides detailed data on each ear’s performance separately.
How it Works?
The PTA test works by delivering calibrated pure tones via two methods: air conduction through insert earphones or supra-aural headphones, and bone conduction using a vibrator placed behind the ear on the mastoid bone. This makes PTA the most accurate PTA test for ear health assessment, as it checks sound transmission across the entire auditory pathway. The audiologist starts at an audible level and decreases intensity in 5-10 dB steps until the patient no longer responds, then ascends to find the threshold. Responses are consistent across octaves (e.g., 500, 1000, 2000, 4000 Hz), ensuring accuracy in identifying frequency-specific weaknesses.
What PTA Measures?
PTA checks how soft a sound you can just barely hear at different pitches in each ear. It shows your “hearing score” in decibels (dB), from normal hearing to mild, moderate, or severe loss. This helps the audiologist see if both ears hear equally or if one ear is weaker.
What PTA Does Not Measure?
PTA does not show how clearly you understand words, how well your middle ear is working, or how healthy your inner ear hair cells are. It also cannot detect how your brain processes sound or how loud sounds feel uncomfortable, so other tests are needed for a complete hearing check.
PTA Test Significance – Uses, Benefits & Indications
The PTA test plays a key role in protecting hearing health by spotting problems early, preventing worsening, and improving daily life through customized care plans.
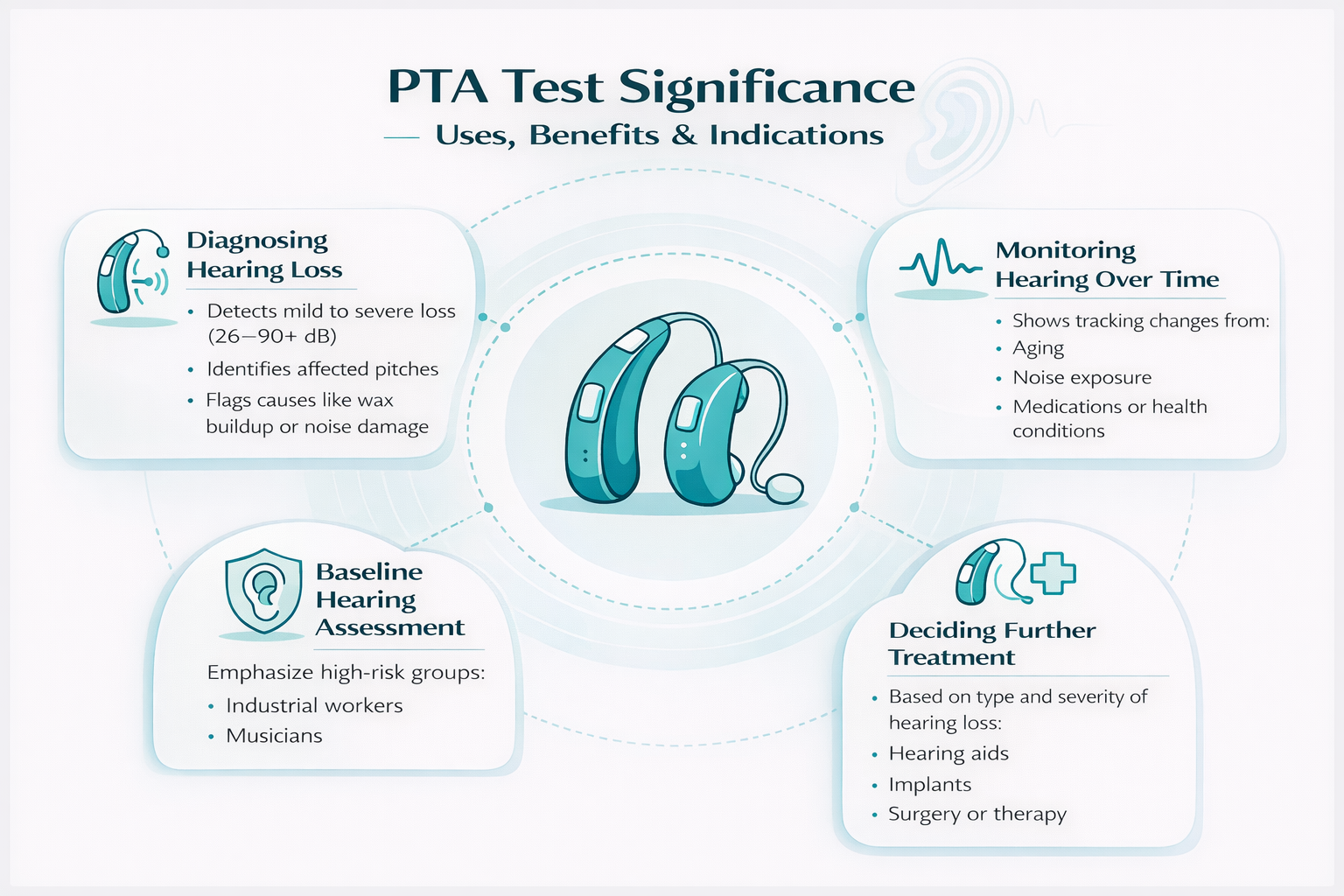
- Diagnosing Hearing Loss: Spots mild to severe loss (26-90+ dB) before speech issues appear, identifying affected pitches and causes like wax or noise damage for quick referrals.
- Monitoring Hearing Over Time: Tracks changes from aging, noise, meds, or health issues via repeat tests, spotting trends to adjust habits or aids early.
- Baseline Hearing Assessment: Records starting hearing levels for high-risk groups like workers or musicians, catching shifts fast in check-ups.
- Deciding Further Treatment or Hearing Support: Guides choices for hearing aids, implants, surgery, or therapy based on loss type and severity.
How Do You Know It’s Time to Get a Pure Tone Audiometry Test?
Recognizing early signs of hearing issues prompts timely PTA testing, preventing progression and preserving communication skills. Consult an audiologist if symptoms persist.
Common Signs and Symptoms
- Difficulty hearing in noisy environments: Struggling with conversations at parties or restaurants despite others hearing clearly.
- Frequent requests for repetition: Asking people to repeat themselves often, especially for high-pitched voices or consonants like “s” or “th”.
- Turning up TV or phone volume: Needing louder volumes than family members, even for familiar shows.
Risk Factors Warranting Testing
- Age-related changes: Over 50, or family history of early hearing loss (presbycusis).
- Noise exposure: Long-term work in loud settings, concerts, or headphone overuse without protection.
- Health conditions: Diabetes, heart disease, ototoxic medications, or recent ear infections/trauma.
When to Act Promptly
Schedule a pure tone audiometry test if symptoms interfere with daily life, work, or relationships—early detection via PTA can reverse treatable causes or fit aids effectively.
Step-by-Step: What Happens During a PTA Test
The pure tone audiometry test is a simple, non-invasive process usually completed within 20–30 minutes. Here’s what to expect:

-
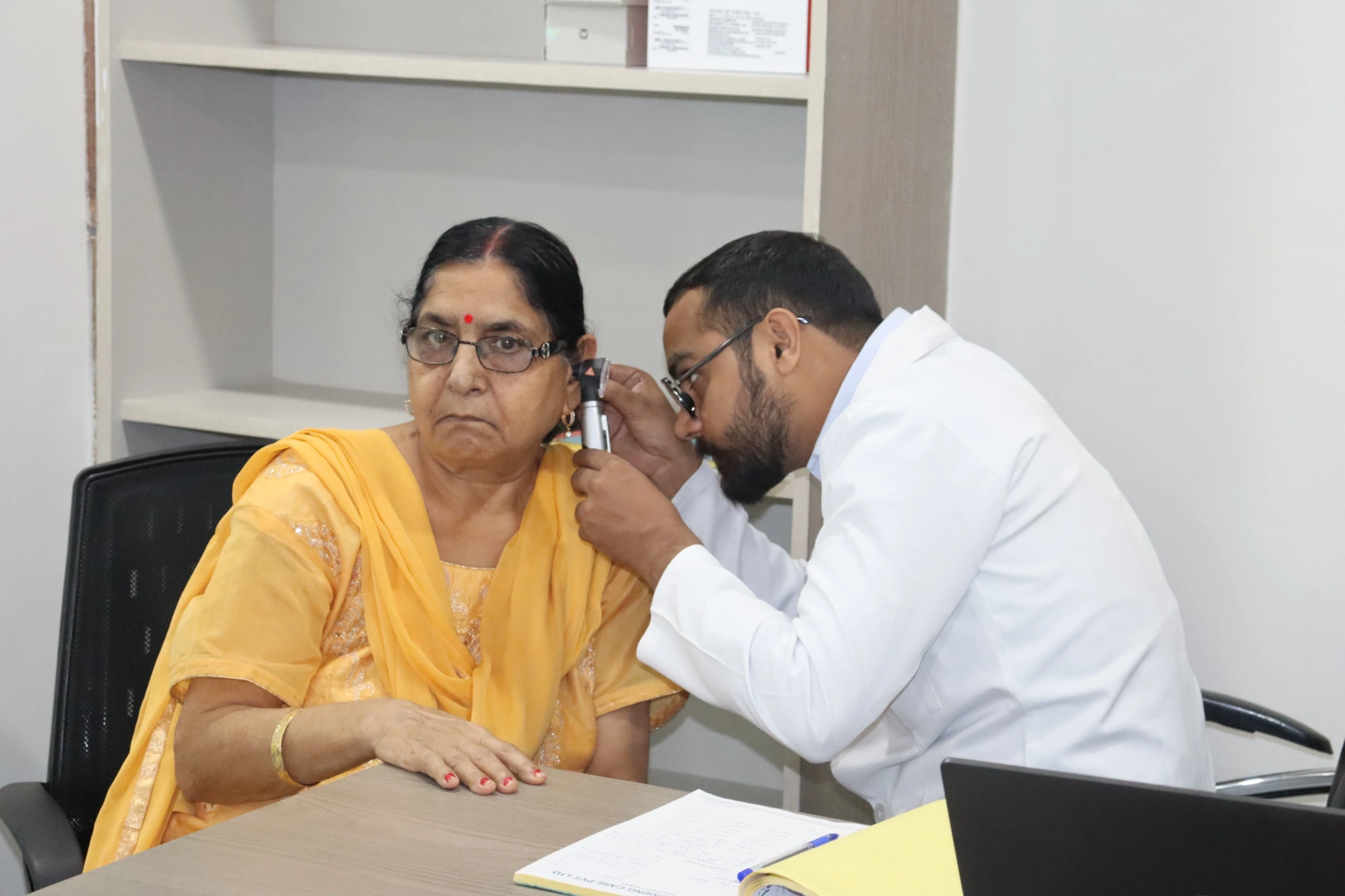
Pre-test: medical/ear history + visual ear check (otoscopy)
The audiologist begins by asking about ear issues, medications, and hearing concerns, followed by inspecting the ear canal for wax buildup or infections.
-
Environment: sound-treated room
Testing takes place in a soundproof booth to eliminate background noise and ensure accurate threshold detection.
-
Air Conduction Testing
Tones are presented through headphones. The patient signals each time a sound is heard. This assesses the entire hearing system – outer, middle, and inner ear.
-
Bone Conduction Testing
A small vibrator is placed behind the ear to measure inner ear (cochlear) hearing directly, bypassing the outer and middle ear.
-
Recording results
Responses are plotted on an audiogram test, visually showing the degree of hearing loss across frequencies.
-
Post-test review
The audiologist explains results, discusses their meaning, and suggests suitable next steps such as hearing aids or further ENT consultation.
Interpreting Results: What the Audiogram Tells You & Types of Hearing Loss?
-
- Audiogram axes explanation: The horizontal axis shows frequency (pitch in Hz), and the vertical axis shows intensity (loudness in dB).
- Normal hearing range vs hearing loss thresholds: Hearing within 0–25 dB is normal; higher thresholds indicate varying degrees of hearing loss.
Types of hearing loss:
-
- Conductive: Outer or middle ear blockage or malfunction.
- Sensorineural: Inner ear or nerve damage.
- Mixed: Combination of both.
- Audiogram patterns and indications: Sloping, flat, or notch-shaped curves may indicate age-related loss, noise exposure, or specific medical conditions.
Understanding Hearing Loss Levels on an Audiogram: Where Everyday Sounds Fit. The audiogram does more than show hearing thresholds – it maps real-world sounds across different loudness and frequency levels. This helps patients understand how hearing loss affects everyday listening.
Most daily speech and environmental sounds fall between 250 Hz and 6000 Hz in pitch and 20 dB to 60 dB in loudness. This is where meaningful communication happens – from whispering to normal conversations.
Examples of Real-World Sounds on an Audiogram
| Frequency Type | Typical Sounds | What It Means for Hearing |
|---|---|---|
|
Low-frequency range (250–1000 Hz) |
Vowels (“a,” “o,” “u”), motor sounds, drums |
People with low-frequency loss may feel voices sound “muffled” or “far away.” |
|
Mid-frequency range (1000–3000 Hz) |
Everyday speech, phone conversation, doorbell |
Difficulty following conversations, especially in noise. |
|
High-frequency range (3000–8000 Hz) |
Consonants (“s,” “f,” “th,” “k”), birds chirping, beeping alarms |
Speech becomes unclear — “I can hear, but I can’t understand.” |
Understanding which frequency range is affected explains why two people with the same “severity” of hearing loss may experience communication challenges differently.
When people see only numbers on an audiogram, it’s difficult to relate it to daily life. Showing where speech, alarms, music, traffic noise, phones, or whispers fall on the frequency graph gives a clearer picture of:
- Why some words sound unclear even if the volume is loud enough
- Why noisy environments make speech harder to follow
- Why both speech therapy and hearing aids must focus on restoring clarity, not just loudness
Severity of Hearing Loss: Understanding What Each Level Means
Hearing loss doesn’t progress the same way for everyone — some people mainly struggle with soft voices, while others may miss everyday speech entirely. The degree of hearing loss is determined by the quietest sound a person can hear (in decibels – dB HL) during a pure tone audiometry test. Understanding these levels helps patients and families know what to expect in daily communication and what support might be needed.
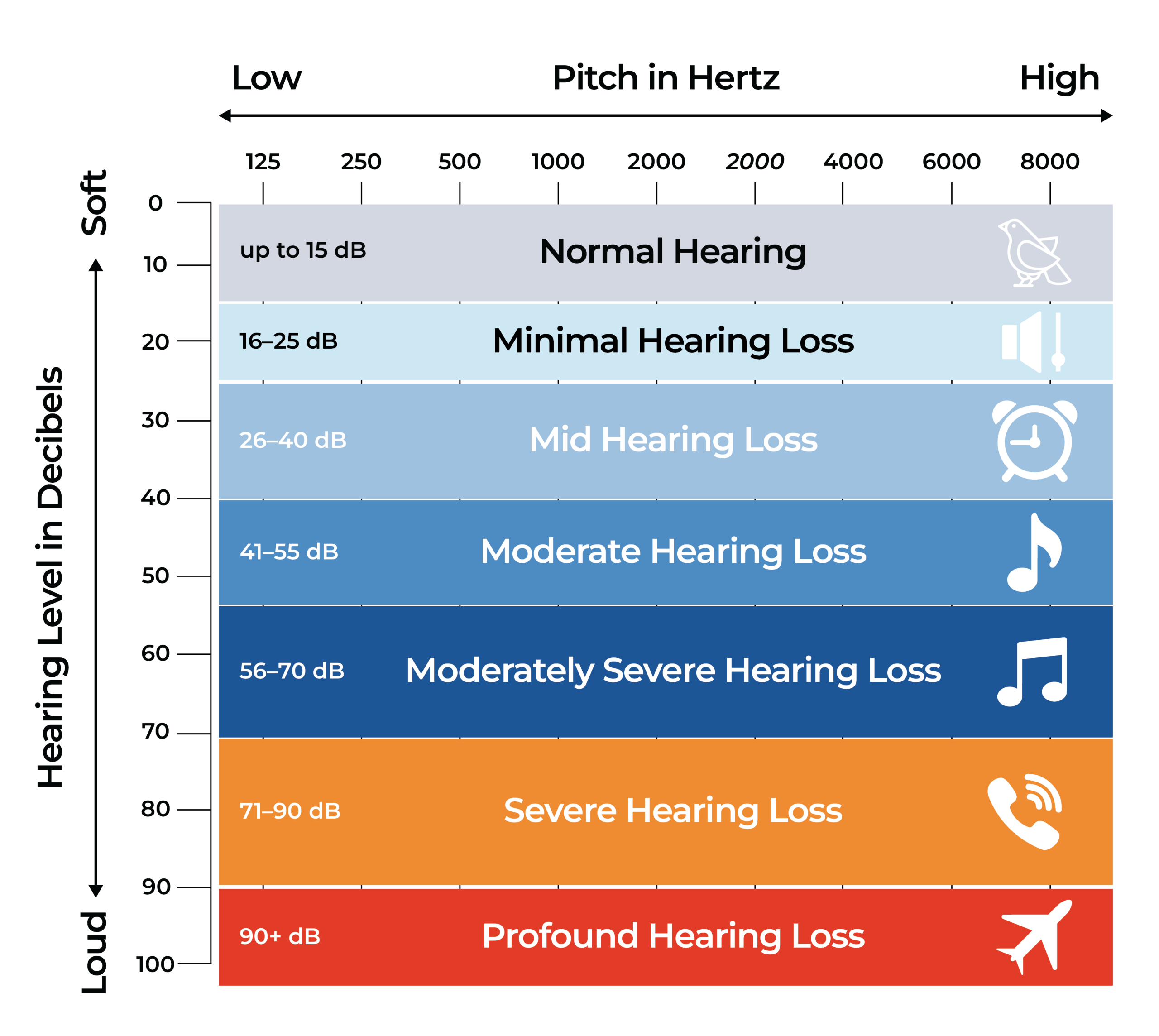
| Degree of Hearing Loss | Hearing Threshold (dB HL) | Description | Real-Life Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Normal Hearing | 0 – 15 dB | No hearing loss | Hears whispers, soft speech, and everyday sounds clearly in all environments. |
| Mild Hearing Loss | 26 – 40 dB | Slight difficulty | Trouble hearing soft voices and consonants in noisy environments. |
| Moderate Hearing Loss | 41 – 55 dB | Noticeable difficulty | Needs speech to be louder; often asks people to repeat. |
| Moderately Severe Hearing Loss | 56 – 70 dB | Significant difficulty | Group conversations become challenging without hearing aids. |
| Severe Hearing Loss | 71 – 90 dB | Major difficulty | Cannot hear speech without amplification. |
| Profound Hearing Loss | 91 dB and above | Very severe difficulty | Requires cochlear implants or assistive technology. |
Why Severity Matters?
Knowing the degree of hearing loss does more than label a condition — it determines the next step in care.
For example:
- Mild or moderate loss may benefit from early hearing aid fitting to prevent communication fatigue.
- Severe or profound loss requires medical evaluation and advanced solutions like cochlear implants.
- Tracking the degree over time helps monitor whether hearing is stable or worsening.
Benefits of the PTA Test: Why It’s Essential for Detecting Hearing Loss
- Non-invasive, painless, quick: PTA only involves listening and responding to soft beeps, with no needles or instruments inside the ear, and is usually completed within about 20–30 minutes.
- Frequency-specific: It checks hearing at individual pitches across the speech range, so the audiologist knows exactly which frequencies are affected and how this impacts real-life listening.
- Identifies type and degree of hearing loss: By comparing air- and bone-conduction results, PTA shows whether the loss is conductive, sensorineural, or mixed, and how mild, moderate, severe, or profound it is.
- Baseline and monitoring tool: The test creates a clear starting record of hearing that can be repeated over time to catch early changes from age, noise exposure, or medications.
- Widely accepted standard: PTA is the globally recognized reference test for hearing thresholds, so its results are trusted and comparable across clinics and specialists.
Pure Tone Audiometry Test Cost & Pricing in India
At Anand Care, we believe hearing evaluation should be accessible and transparent for every patient. Our Pure Tone Audiometry (PTA) test price is designed to be affordable while ensuring the highest diagnostic accuracy and comfort.
Current Pricing for PTA Test at Anand Care
- Chandigarh, Delhi, Gurgaon & Noida, it is 800/- (report is provided at the same time, done using international standards by an experienced audiologist)
- Patiala & Jalandhar is 600/-
- Ludhiana is 700/-
The fee includes:
- Pure Tone Audiometry test
- Detailed report provided immediately
- Assessment using calibrated, international-standard equipment
- Testing done by qualified and experienced audiologists
We also offer:
- UPI, Card, and Cash accepted.
PTA vs Other Hearing Tests
Pure tone audiometry provides threshold data, while other tests assess different aspects like speech clarity.
| Test | Focus | Key Difference from PTA |
|---|---|---|
| PTA Test | Pure tone thresholds | Frequency-specific sensitivity |
| Speech Audiometry | Word recognition | Measures understanding, not just detection |
| Tympanometry | Middle ear function | Objective; no patient response needed |
| Otoacoustic Emissions (OAE) | Inner ear response | Automated screening for infants and adults |
How to Prepare for a Hearing Test?
Proper preparation ensures accurate pure tone audiometry test results, minimizing temporary factors that could skew thresholds. Follow these steps for a smooth experience.
- Avoid loud noise exposure 24 hours prior: Skip concerts, loud machinery, or high-volume headphones to prevent temporary threshold shifts (TTS) that mimic hearing loss and invalidate baseline data.
- Inform about medications, ear infections, or recent illnesses: Disclose ototoxic drugs (e.g., certain antibiotics), colds, or ear issues, as they impact middle ear function or responses-your audiologist may reschedule if needed.
- Rest well; fatigue can affect responses: Get a good night’s sleep, as tiredness reduces concentration and leads to inconsistent signaling during tone presentation.
- Remove hearing aids or devices unless instructed: Arrive without aids, plugs, or earrings to allow clear headphone placement and unbiased natural hearing measurement.
- Arrive with questions about pure tone audiometry test price or process: Note concerns like costs, duration, or follow-ups beforehand for a productive consultation post-test.
 |
 |
Why Patients Choose Anand Care for Pure Tone Audiometry?
At Anand hearing Care, PTA is conducted by expert audiologists using advanced clinical-grade audiology equipment inside sound-treated rooms to ensure precision and comfort. Our team focuses on accurate diagnosis with patient-first care. Our PTA test price is designed to be affordable while ensuring the highest diagnostic accuracy and comfort. Patients searching online for “pure tone audiometry test price” or similar terms often choose us because the fee includes a complete evaluation conducted by qualified audiologists.
Post-test, every patient receives a detailed counselling session explaining the audiogram, the degree and type of hearing loss, and treatment recommendations — whether it’s medical care, hearing aids, or follow-up monitoring. Transparent pricing, compassionate support, and long-term care make us a trusted choice for families.
Conclusion
Pure Tone Audiometry (PTA) is an essential, dependable test for identifying hearing loss early and planning timely treatment. Whether someone struggles with conversations, hears ringing sounds, or suspects age-related decline, a pure tone audiometry test can provide the clarity needed to protect hearing health. If you’re experiencing symptoms, don’t delay – schedule your PTA test and take the first step toward better hearing and improved quality of life.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: Is a PTA test painful?
No, a pure tone audiometry (PTA) test is not painful; it is non-invasive, uses only headphones or a small vibrator, and simply requires you to respond to soft sounds.
Q: What is the purpose of a PTA test?
The pure tone audiometry test measures your hearing thresholds at different frequencies to detect hearing loss, determine its severity, and guide decisions about treatment or hearing aids.
Q: What is the normal range for pure tone audiometry?
In a PTA test, normal hearing typically falls between about -10 dB and 20 dB hearing level across the main speech frequencies in both ears.
Q: What is a good audiometry score?
A good pure tone audiometry result shows thresholds in the normal range (around -10 to 20 dB HL), indicating you can hear soft speech and everyday sounds clearly without difficulty.
Q: How long does a pure tone audiometry test take?
A standard pure tone audiometry test usually takes 15–30 minutes, depending on your responsiveness and whether both air- and bone-conduction measurements are performed.
Q: What are the 4 types of hearing loss?
The main types of hearing loss identified with a PTA test are conductive, sensorineural, mixed (a combination of both), and central (problems with the auditory pathways or brain).
Q: Why is a PTA test performed?
A pure tone audiometry test is performed to diagnose hearing loss, classify its type and degree, monitor changes over time, and plan suitable interventions such as hearing aids or medical treatment.
Q: Is a PTA test painful?
No, the PTA test is completely painless and comfortable; you only listen to beeps or tones and press a button or raise your hand whenever you hear a sound.
Q: Where can I get a Pure Tone Audiometry (PTA) test in Chandigarh?
You can get a Pure Tone Audiometry test at Anand Hearing Care, Chandigarh, conducted by experienced audiologists in a sound-treated room using calibrated international-standard equipment.
Q: Can I walk in for a PTA test in Patiala or is an appointment needed?
Walk-ins are usually accepted, but booking an appointment in advance is recommended for quicker testing and minimal waiting time.



